what is cancer
 |
| what is cancer |
1. Introduction (what is cancer)
In the work presented below is a very important issue as it is cancer, which is a causative agent of deaths worldwide.
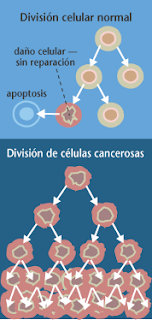
Cancer is any malignant tumor is characterized by an abnormal multiplication of cells and disorganized, which have the characteristic of invading adjacent tissues (metastasis).
The main attribute of malignant tumors is their ability to spread beyond the site of origin. The invasion of neighboring tissues may occur by extension or infiltration, or distance, producing secondary growths known as metastasis. The location and route of spread of metastases varies with primary cancers.
The more aggressive malignant cancer is a less resembles the structure of the tissue from which, but the rate of growth of cancer depends not only on cell type and degree of differentiation, but also dependent on the host factors. A feature of malignancy is the tumor cell heterogeneity. Due to changes in cell proliferation, cancer cells are more susceptible to mutation.
2. Cancer (Definition)
Cancer: A tissue growth produced by the continuous proliferation of abnormal cells capable of invasion and destruction of other tissues.
Cancer, which may originate from any type of cell in any tissue, not a single disease but a group of diseases that are classified according to the tissue and cell of origin. There are several hundred different ways, with three main subtypes of sarcomas come from connective tissue such as bone, cartilage, nerves, blood vessels, muscles and adipose tissue. Carcinomas derived from epithelial tissues such as skin or epithelia that line the body cavities and organs, and glandular tissue of the breast and prostate. Carcinomas include some of the most common cancers. Carcinomas of similar structure to the skin are called squamous cell carcinomas. Those with a glandular structure are called adenocarcinomas. In the third subtype are leukemias and lymphomas, including cancers of tissues forming blood cells. Cause inflammation of the lymph nodes, invasion of the spleen and bone marrow, and overproduction of immature white cells.
Cancer is not contagious.
Tipe of cancer (Percent of all cancers)
3. Origin of cancer
Certain factors are capable of causing cancer in a proportion of individuals exposed to them. These include heredity, chemicals, ionizing radiation, infection or viruses, and trauma. Researchers study how these different factors may interact in a sequential manner to produce multifactorial and malignant tumors. Cancer is, in essence, a genetic process. Genetic alterations can be inherited, or produced in a cell by a virus or an injury caused externally.
Inheritance: It is estimated that 5 to 10% of cancers are hereditary. Some forms of cancer are more common in some families, breast cancer is an example. Colon cancer is more common in families with a tendency to have colon polyps. A form of retinoblastoma appears only when a specific gene is absent. These genes, called tumor suppressor genes or anti-oncogenes, in normal conditions prevent cell replication. Their absence removes the normal control of cell division. In some inherited disorders, chromosomes have an intrinsic fragility, these processes involve a high risk of cancer.
Chemicals: Coal tar and its derivatives are considered to be highly carcinogenic. Its vapors in some industries (eg refineries) are associated with the high incidence of lung cancer among workers
Today it is known that benzopyrene, a chemical present in coal, causes skin cancer in people whose jobs are related to coal combustion.
Arsenic is associated with lung cancer, as workers of copper and cobalt mines, smelters and factories of insecticides have an incidence of this cancer greater than normal. Workers in the asbestos-related industries, the incidence is up to 10 times more than normal.
A substance produced by the fungus Aspergillus flavus, called aflatoxin, which contaminates food and poorly preserved, causes liver cancer in some animals. It has been found that in countries where food contamination by molds is common, the incidence of liver and stomach cancer is high.
Smoking is another carcinogen, has determined that lung cancer death is 6 times higher among smokers than among nonsmokers. The cigarette is as harmful because it contains substances, nicotine, acids and oxides of carbon and tar.
Alcohol is also a major sponsor, its chronic abuse significantly increases the risk of cancers that are induced by other agents.
Radiation: Ionizing radiation is one of the most recognized causal factors. Radiation can cause changes in DNA, such as breakage or chromosomal transpositions in which the broken ends of two chromosomes can be exchanged. The radiation acts as an initiator of carcinogenesis, inducing alterations that progress to cancer after a latency period of several years. The sun's ultraviolet rays and X-rays increase the propensity to get skin cancer and leukemia. Lso excessive exposure to sunlight, by people with white skin, increases the risk.
Or virus infections: There is increasing evidence that some infections can eventually cause cancer, and in particular those related to cancers of the stomach, liver, cervix and Kaposi sarcoma (a special type of cancer that occurs in patients AIDS). It has linked the bacterium Helicobacter pylori with stomach cancer. Several studies show that people infected with this bacterium are four times more likely to develop this cancer.
Viruses are the cause of many cancers in animals. In humans, the Epstein-Barr virus associated with Burkitt lymphoma and lymphoepitheliomas, virus hepatitis with hepatocellular carcinoma and type II herpes or genital herpes with cervical carcinoma. All of these viruses associated with human tumors are of the DNA. HTLV virus, however, is of type RNA, or retroviruses, like most of the viruses associated with tumors in animals. Produces a human leukemia. In the presence of an enzyme called reverse transcriptase, induces the infected cell to produce DNA copies of the genes of the virus, thus incorporated into the cellular genome. These RNA virus containing a gene called viral oncogene capable of transforming normal cells into malignant cells. Research has shown that viral oncogenes have a counterpart in normal human cells: the proto-oncogene, or cellular oncogene. The products of oncogenes (the proteins they produce) are growth factors (or proteins necessary for the action of such growth factors), which stimulate the growth of tumor cells
Trauma: It is considered detrimental mechanical irritation produced on a portion of the skin and the friction exerted on moles. Lip cancer in pipe smokers is associated with chronic irritation caused by the pipe about a group of cells in the lip. In India, a high incidence of cancer of the abdomen and groin is related to the dress (a sort of loincloth) of widespread use.
4. Cancer Prevention
It is very important the fact that many are considered carcinogenic agents are manageable by man. In this sense, to know the relationship between a cancer and a particular factor, we can direct our actions towards the elimination of the agent.To this end measures should be taken as:
No smoking
Avoid exposure to the sun for prolonged periods (especially people with white skin or sensitive).
Maintain adequate genital hygiene.
Control the consumption of alcoholic beverages. Avoid excesses of drinks.
A proper diet rich in vegetable fibers, fruits and low in fat.
In broad risk groups such as workers in certain industries, should take appropriate precautions to protect and maintain medical control.
Avoid exposure to radiation (X-rays, etc.). It eventually can cause disorders.
In his early studies can be said that 50% of the cancers are curable, hence the importance of early diagnosis dl.Metastatic invasions usually occur when the primary tumor has already acquired a considerable size, the length of time depends on the type of tumor, some are very rapid as testicular cancer, others of ten or more years (some types of cancer thyroid), but most often the tumor reaches its full development within five years.
5. Cancer diagnosis (methods)
It's invaluable help they have given the modern techniques of detection in the fight against cancer. Among the tests commonly performed to rule out tumors including:Uterus: Cervical cytology or Pap test is a simple, fast, painless and involves taking a sample of cervical secretions for some cells and spread on a slide. Is processed in the laboratory by binding techniques, and then study them under a microscope. This test not only indicates whether cancer is suspected, but the presence of some other infection.Who should get tested?, We recommend that every woman who has had sexual relations practice will review periodically (once a year or every 2 years) or the doctor.
There are other tests such as:Determination of malignant cells in blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid (the latter in case of brain tumors).Scan (use of radioactive isotopes).EchosonographyComputed tomography (consisting of Ogano trasnsversales cuts to study).Magnetic resonance imaging (very recent use)
LOCATION
TYPE OF REVIEW
Uterus
Cervical cytology or Pap
Mama
Breast Self-Examination
Clinical examination
Mammography (x-ray study).
Stomach
Double contrast radiology
Lung
Radiology
Sputum cytology
Bronchoscopy.
6. Cancer Treatment
The traditional therapeutic measures include surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. In the present study the utility of immunotherapy and modulating the biological response.
Surgery: The primary strategy for curative treatment of cancer is the excision of all malignant cells by surgical intervention. In the past, this involved the excision of all affected tissue and the maximum number of potentially affected tissues, including the surrounding tissues and lymph nodes. For some tumors, especially breast cancer, it is not necessary as ablative surgery (mastectomy) in most cases. Improvements in surgical techniques, knowledge on physiology, anesthesia and the availability of potent antibiotics and blood products, have led to more limited surgery, with fewer sequels and more speedy recovery. However, many cancers are too widespread at the time of diagnosis for curative surgery is possible. If the local extent of tumor affects surrounding tissues that can not be resected, or if there are distant metastases, surgery is not curative treatment. However, it may be beneficial for symptomatic relief of certain situations such as obstruction, or may have in order to reduce the tumor mass to allow better response to chemotherapy or radiotherapy thereafter.
Radiation: Ionizing radiation can be electromagnetic or particulate and produce tissue destruction. Electromagnetic radiation includes gamma rays, a form of radioactive emission, and X-rays, which occur when an electron beam hits a heavy metal. Particle radiation include electron beam, protons, neutrons, alpha particles (helium nuclei) and pions.
The sensitivity of tumors to radiation varies widely. Sensitive tumors are those whose sensitivity is higher than the normal surrounding tissues. When such tumors are also accessible, superficial tumors or tumors in organs like the uterus in which you can enter a radiation source, can be cured by radiotherapy. The property of the radiation to some extent respect normal tissues allows the treatment of tumors in locations where surgery is not possible by the proximity of vital tissues or because the tumor has begun to infiltrate adjacent structures that can not be sacrificed. Radiation therapy is often used as a palliative treatment, especially in metastases.
Radiation therapy may be useful as an adjunct to surgery. Preoperative radiation may sterilize tumor cells rapidly and prevent its spread during surgery. You can also reduce tumor surgery facilitating or turning an inoperable tumor in another operable. In other cases, radiation therapy is used postoperatively.
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to treat cancer. Because drugs are distributed in the body through the circulatory system, chemotherapy is useful for those whose tumors spread makes them inaccessible to surgery or radiotherapy. There are many anticancer drugs, most of which act by interfering with the synthesis or function of DNA. Thus the dividing cells are more sensitive to chemotherapy.
The sensitivity of certain tumors to chemotherapy is such that it is possible to cure a high percentage: this happens in uterine cancer, acute leukemia (especially in children), Hodgkin's disease and diffuse large cell lymphomas; testicular carcinoma, ovarian carcinoma, small cell carcinomas of the lung, and much of childhood cancers. Often these processes have spread cancer at diagnosis and no other therapeutic option. Other advanced cancers have good response to chemotherapy and can be controlled for long periods, so it is often used as palliative treatment.The two main problems that limit the use of chemotherapy are toxicity and resistance. Techniques that prevent or control the toxicity and decrease the risk of resistance have been refined. It is important to the early start of treatment, the use of optimal doses of drug, the repeated cycles with short intervals if possible, provided that allows the patient's recovery from the toxic effects.Hormone therapy: Many cancers from tissues that are sensitive to hormones, such as breast, prostate, endometrium and thyroid, respond to hormonal treatment. Involves the administration of various hormones or antihormones or termination of the corresponding stimulating hormone.
Skin cancer. Risk Factors
Prolonged exposure to sun, wind or cold temperatures. The risk increases in people of white or light skin.
Exposure to irritating chemicals such as arsenic, petroleum, coal, paraffin, especially by workers in these industries.
Scars caused by injury or severe burns.
Exposure to X rays and radiation from other radioactive materials.
Symptoms: People who are exposed to the risk factors mentioned must pay attention to chronic sores or irritations that do not heal, moles and other birthmarks to increase in size or change color.Prevention: As preventive measures to use sunscreen and avoid sun exposure for a long time, especially if you have sensitive skin and very white.
Clothing should be suitable for protection from sun, wind or cold as appropriate.Moles and warts removed surgically is recommended and burns, fistulas, etc., Should receive proper treatment to heal. Chronic irritation should be avoided on a body part (such as that occurs on the lip of the pipe smoker).
Diagnosis: annual medical examination. Frequent observation itself sensitive areas of your skin, especially moles, scars and birthmarks.
Cancer of the uterus. Risk Factors
Sex at an early age.
Sex with different individuals.
Having had sexually transmitted diseases, herpes, etc. ..
Have presented abnormal cytology.
Symptoms: Investigate any irregular vaginal bleeding or unusually long, as well as small spots or bleeding after intercourse.
Diagnosis: Cervical cytology has been helpful for early diagnosis of cancer. It involves taking a sample of the discharge from the cervix to examine the cells present. The sample was spread on a sheet, is applied laboratory techniques of fixation and staining and then observed under a microscope.
Prevention: As a preventive measure is indicated make an annual medical examination and cervical cytology (also called Pap smear). Any woman who has been sexually active ouch over 18 years should be practiced such control.
Other prevention measures include delaying the onset of sexual activity and sexual intercourse with an individual.
Lung cancer. Risk Factors
Use of snuff.
Frequent exposure to environments where chromium compounds, nickel, petroleum, uranium, arsenic air pollutant ..
Asbestos.
Silica.
Personal history of ovarian or endometrial cancer.
Frequent therapy based on estrogen (female hormone).
Symptoms: You must be alert to persistent cough, shortness of breath and chest pain. Just as with any change in volume, odor, or blood in the sputum.
Diagnosis: People exposed to the risk factors mentioned must undergo an annual medical examination and radiological control of the lung, also should be tested frequently in the sputum.Prevention: Measures of prevention, the most important today is the cessation of smoking. The increase of people with lung cancer is almost 75% the use of snuff.
In industries where workers are exposed to carcinogens in the environment, must take security measures for their protection and that the incidence of lung cancer among them is very high, especially if they are smokers.
Cancer of the stomach. Risk Factors
People with reflux esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus from irritation caused by reflux of gastric juice of the stomach).
Lack of secretion of gastric juice.
Chronic gastritis.
Gastric ulcer.
Abuse of snuff and alcohol.
Symptoms: These are important signs, loss of appetite, dark stools (black) and difficulty swallowing. Other signs are inflammation of the gastric mucosa or chronic gastritis and weight loss. They are more exposed men and women over 35 years.
Prevention: As a preventive measure to be taken into account diet, it must be balanced, low in fat and rich in fruits, grains and vegetables. Alcohol is a frequent cause of gastritis. Avoid eating food often balances, smoked, fried, etc..
People with digestive tract problems such as ulcers, polyps, gastritis, stomach or operated frequently, should have regular medical checks. In Venezuela, this allo-risk areas with the highest incidence of the disease: New South Wales, Tachira, Merida, Trujillo and Lara.
Cancer of the prostate. Risk Factors
The incidence increases with age especially after 50 years.
Although prostate problems begin after age 50, is 65 when they present the most severe cases.Symptoms: Cancer of the thyroid is very common and should be given due importance to the symptoms because the onset of cancer usually does not report any evidence at first. The first symptoms are dificultas to urinate, blood in urine and need to urinate several times at night.
Diagnosis: Consultation with a specialist is needed for diagnosis. A medical examination usually includes: digital rectal examination, physical examination and laboratory tests.
Prevention: As a preventive measure, regulate prostate examination is necessary after 50 years. Since the results for early diagnosis of the disease are generally satisfactory.
Breast cancer. Risk Factors
The causes of breast cancer are not well understood yet. But, according to the accumulated experience as doctor visits can be attributed to the following factors:
Are more susceptible to cancer and obese women who have children after age 30.
Those with chronic lesions in the breast.
Family history of breast cancer.
Personal history of breast cancer.
Early menarche and late menopause.
Symptoms: Pay attention to any discomfort, pain, lump or thickening of the breast or armpit that does not disappear for several days. Another warning sign is the discharge from the nipple and sinking it. Retracted or dimpled skin puckered.
Diagnosis: Any woman can practice self-examination and thereby maintain control over any abnormality is present, this can be done five days after menstruation each month.Any abnormalities should be discussed with a doctor.
Should be done yearly physical examination. Every woman should do BSE of the breasts as they let you know and any abnormalities detected early.
7. Conclusion (what is cancer)
The most effective in cancer prevention is to eliminate the consumption of snuff, and that 30% of cancer deaths are caused by consumption. The control diet also reduces mortality: reduce calorie intake to avoid obesity, reduction of calories from fat to 20% of the diet, decreased consumption of red meat, increased intake of fiber (cereal , fruits and vegetables) and protective foods (containing vitamins C and A, vegetables like cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli or Brussels sprouts). Should be limited consumption of smoked foods, salted or rich in nitrite, and alcohol consumption.
Control of environmental factors includes the elimination of carcinogens in the workplace and home, such as eliminating exposure to asbestos fibers or reducing radon in homes.
Screening techniques can be performed for cervical cancer (cervix), breast, colon, rectum and prostate. It is advisable to carry out an annual check from age 40 even in the absence of symptoms, the countries with public health system do not always provide this service and the patient must bear the expense. Breast cancer is considered a major health problem in developed countries and many women die each year from this cause. Women over 50 are at the greatest risk of developing breast cancer and the maximum risk is presented by patients older than 75 years. Cytology has proven an effective method for early detection of cervical cancer. We recommend performing a Pap smear every 3 years if it has been detected 2 negative smears at yearly intervals. In many developed countries the increase in the number of people who enjoy their holidays in hot countries has been an increase in skin cancer. Recommended preventive measures, such as creams or shields against potentially harmful action of solar ultraviolet rays.
The widespread adoption of early detection measures could reduce the incidence of breast and colon cancer, and increase the cure rate of breast cancer, colon, rectum, cervix and prostate.
copyrigh 2012 what is cancer

0 comentarios:
Publicar un comentario